History
History
A chronology of the history of NHK Spring.
Click the + on the far right to see the list.
-
1930s
1939 September: NHK Spring is established with capital of JPY 1,500,000.
-
1940s
1940 November: Yokohama Plant starts operation. (Isogo Ward, Yokohama)
1943 December: Ina Plant starts operation. -
1950s
1958 May: Merger with Daido Spring Co., Ltd. which becomes Kawasaki Plant (Suspension Springs).
-
1960s
1961 May: Kawasaki Plant (Precision) is newly established.
1961 June: Nagoya Plant (current Toyota Plant) is newly established.
1962 March: Technical assistance agreement related to seat springs is concluded with the American company Rockwell.
1962 December: Kawasaki Plant (Seating) is newly established.
1963 December: NHK Spring (Thailand) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in Thailand.
1965 December: Rockwell acquires an equity stake in the company.
1969 July: Ota Plant (currently a branch factory of Gunma Plant) is newly established.
1969 September: Uni Auto Parts Manufacture Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in Taiwan. -
1970s
1970 May: Atsugi Plant (Industrial Machinery & Equipment) is newly established.
1970 November: Atsugi Plant (Precision) is newly established (relocated from Kawasaki).
1972 September: The capital tie-up with Rockwell is dissolved.
1973 November: Shiga Plant is newly established.
1975 February: NHK Cimebra Indústria de Molas Ltda., a joint venture company, is established in Brazil.
1976 October: NHK International Corporation is established in the United States. -
1980s
1980 September: Eguzkia NHK S.A., a joint venture company, is established in Spain.
1981 December: Komagane Plant (Industrial Machinery & Equipment) is newly established.
1983 November: Komagane Plant (Precision) is newly established.
1986 September: NHK-Associated Spring Suspension Components Inc., a joint venture company, is established in the United States.
1986 December: Gunma Plant is newly established.
1987 May: General Seating of America, a joint venture company is established in the United States.
1987 September: New Mather Metals Inc. is established in the United States.
1987 November: Yokohama Plant (Suspension Spring) is newly established as the first stage of construction of the Yokohama office.
1989 November: Ibérica de Suspensiones, S. L., a joint venture company, is established in Spain. -
1990s
1990 April: Yokohama Plant (Seating) is newly established (relocated from Kawasaki) in Yokohama Office.
1991 February: The main building is newly established at Yokohama Office, and the head office is relocated from Isogo.
1993 March: Isehara Plant is newly established (relocated from Atsugi).
1994 July: NHK Manufacturing (Malaysia) SDN. BHD. is established in Malaysia.
1994 October: NHK Precision (Thailand) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in Thailand.
1994 December: NHK Spring (Hong Kong) Co., Ltd. is established in Hong Kong.
1995 November: Chongqing Qingling NHK Seat Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in China.
1996 July: Fabrini, a joint venture company, is established in Brazil.
1996 October: General Seating (Thailand) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in Thailand. Yasu Plant is newly established (relocated from Komaki).
1998 June: Autrans (Thailand) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in Thailand.
1998 September: NHK Spring India Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in India. Fabrini and NHK Cimebra Indústria de Molas Ltda. are merged in Brazil, resulting in establishment of Rassini-NHK Autopeças Ltda. -
2000s
2000 April: Komagane Plant (Disk Drive Suspension) is established.
2001 October: Faurecia-NHK Co., Ltd. and Faurecia-NHK Kyushu Co., Ltd. are established as joint venture companies with Faurecia, France.
2002 May: NHK-Uni Spring (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in China.
2003 September: Ibérica de Suspensiones, S.L. in Spain is merged with Eguzkia NHK S.A.
2003 October: NHK Spring Precision (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd. is established in China.
2003 November: NHK Spring (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. is established in China.
2004 January: NAT Peripheral (H.K.) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in China.
2005 April: NHK Spring Precision of America Inc. is established in United states.
2005 May: NHK-Associated Spring Suspension Components Inc. becomes a subsidiary, and its name is changed to NHK of America Suspension Components Inc.
2005 October: NHK Spring (Taiwan) Co., Ltd., a joint venture company, is established in Taiwan.
2006 September: General Seating of America Inc. in United States becomes a subsidiary and its name is changed to NHK Seating of America Inc.
2006 November: Topura America Fastener, Inc. in United states a becomes consolidated subsidiary.
2007 July: Stocks of Thai Automotive Seating & Interior Co., Ltd. are sold to Toyota Boshoku.
2009 November: Tokyo Sales Branch and Yokohama Sales Branch are integrated and relocated to newly established Yokohama Minatomirai Sales Branch. -
2010s
2010 April: Toledo Plant of New Mather Metals, Inc. is integrated to Franklin Plant.
2010 November: NHK Seating (Hubei) Co., Ltd. is established in China.
2011 July: NHK Automotive Components India Private Limited is established in India.
2011 November: Regional headquarters NHK Spring (China) Co., Ltd. is established in China.
2012 April: NHK Sales Co., Ltd. and Topura Co., Ltd. become subsidiaries.
2012 May: NHK Seating (Zhengzhou) Co., Ltd. is established in China.
2012 July: SUN NHK Philippines., Inc.(SNP) is acquired. NHK Spring Philippines, Inc.(NSP) is established. NHK F Krishna India Automotive Seating Private Limited is established in India.
2012 October: P.T. NHK F. KBU Indonesia Automotive Seating is established in Indonesia.
2012 December: PT. NHK Spring Indonesia is established in Indonesia.
2013 May: NHK Spring Mexico S.A. DE C.V. is established in Mexico.
2014 March: NHK Spring Europe B.V. is established in Netherlands.
2014 September: NHK Spring Kyushu Co., Ltd. is established. NHK Seating (Chongqing) Co., Ltd. is established in China.
2015 April: NHK Spring Hungary KFT. is established in Hungary. NAT Peripheral (H.K.) Co., Ltd. in China becomes a subsidiary.
2016 February: PT. NHK KBU Seating is established in Indonesia.
2017 July: NHK Seating Mizushima Co., Ltd. is established.
2019 March: Miyada Plant is newly established in Kami-ina, Nagano Prefecture.
2019 September: 80th anniversary.
Turning Points
1. Founding of NHK Spring. Acquisition of Shibaura Spring.
NHK Spring's founding originated with the acquisition of Shibaura Spring in Shibaura, Tokyo. Started by Mr. Masao Nakano as a sole proprietorship, this company started by making springs for automobile repairs and expanded to springs for assembly. Later, the company was reorganized as a corporation.
The company's first Presidents Eikichi Kaede, Kiyoshi Inoue, and Hisashi Sakamoto, focused efforts on springs for automobiles. Exhibiting entrepreneurial spirit, they developed a business plan and started out by acquiring an existing spring factory, which they considered the shortest path.
In February 1939, after acquiring the Nitto Plant of Osaka Steel Works and turning it into a rolling mill for springs, the company's board of directors was reelected at an extraordinary shareholders' meeting. Among the new directors was Kiyotoshi Fujioka, who later became President and CEO. After two capital increases and other changes, on September 8 of the same year, the company name was changed to "NHK Spring Co., Ltd." The company celebrates this day as the anniversary of its founding.
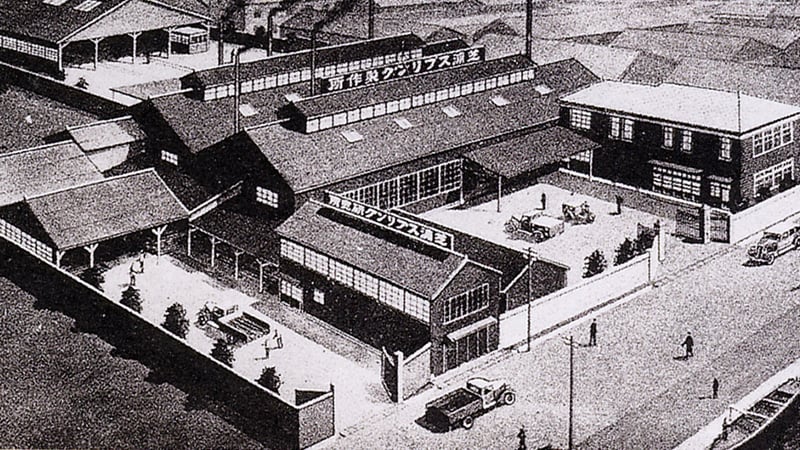
Shibaura Spring - the antecedent of NHK Spring
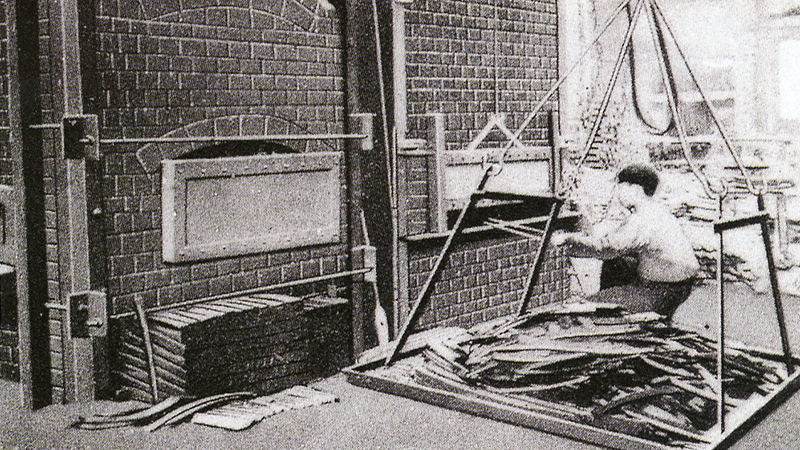
Tempering process
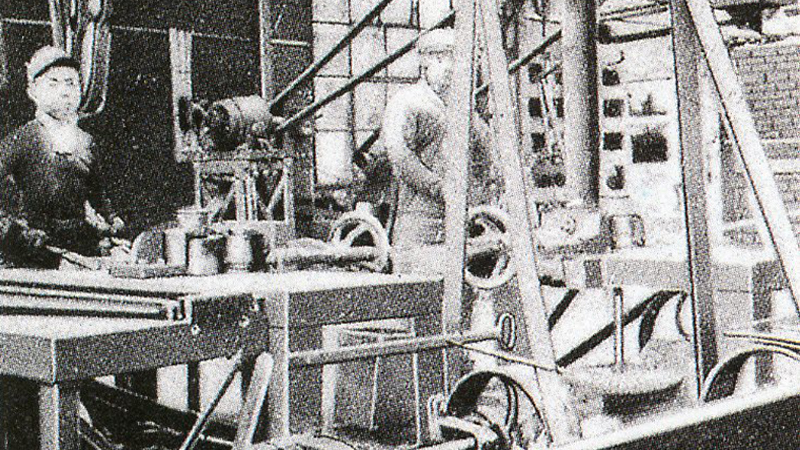
Coil spring processing
2. Relocation from Shibaura to Isogo. Establishment of a state-of-the-art plant.
Although the company was founded in Shibaura, Tokyo, the founders had a vision in their minds to expand facilities and build a large mass-production plant. At that time, since materials and products were mainly transported by ship, they thought it would be best to locate the new plant in a coastal area, so they searched for a site along Tokyo Bay from Ichikawa in Chiba Prefecture. Although they were unable to find suitable land, they did find a reclaimed site in Isogo, Yokohama.
The Company invested a huge amount of money (3 million yen, twice the amount of the Company's capital) in constructing the plant and introducing all possible state-of-the-art equipment, such as cranes, conveyors, and automated machinery. In November 1940, Isogo Factory (see note) began production of leaf springs as a state-of-the-art modernized factory. With the start of operations at Isogo Factory, the Company's headquarters moved to Isogo.
After that, while overcoming the hardships of World War II and so on, the Company continued to develop and innovate production, including the introduction of shot peening, and made great strides on the back of its advanced technological capabilities.
(Note) Isogo Plant was called "Yokohama Plant" at the time, but to avoid confusion with the later Yokohama Plant in Kanazawa Ward, it is referred to here as "Isogo Plant".
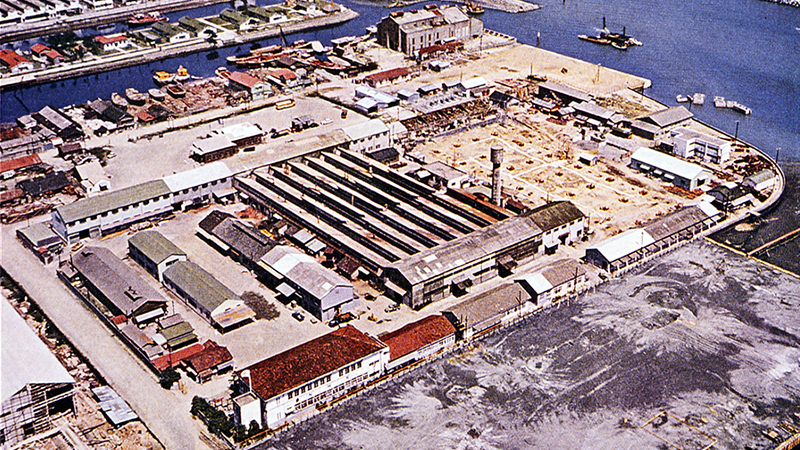

Establishment of a state-of-the-art plant
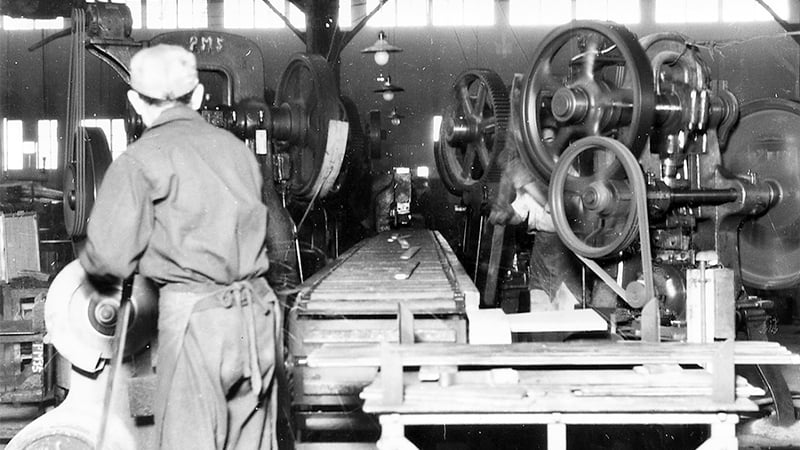

Leaf spring production line equipped with conveyor belts
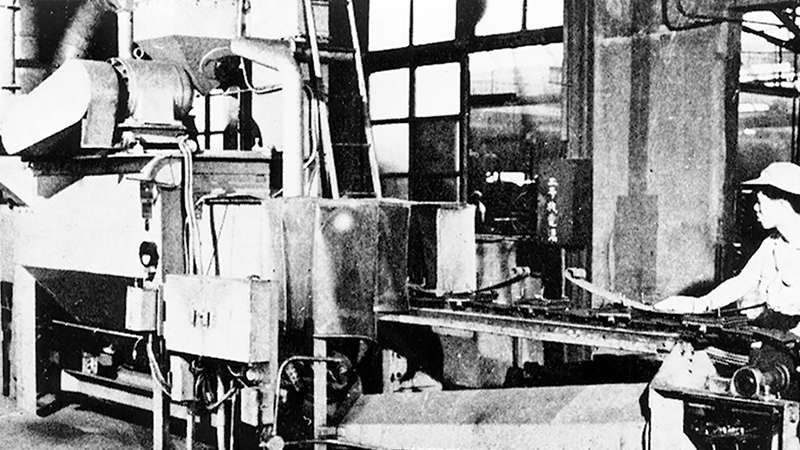
Shot peening introduced in 1959
3. Merger with Daido Spring to become a top spring manufacturer.
The Japanese economy entered a period of full-fledged expansion in tandem with the major economic boom known as the "Jinmu Boom" that began in 1955. Responding to positive capital investment by automobile manufacturers, the Company also promoted capital investment and rationalization over two stages.
Meanwhile, the competition for market share in the spring industry was becoming increasingly intense. In the spring of 1957, fearing that excessive competition could lead to mutual collapse, the Company's management spearheaded a reorganization of the industry. They came to the drastic conclusion of merging with the spring division of Daido Steel, one of the top three spring makers in the industry.
The merger process progressed quickly, and after repeated negotiations with the Fair Trade Commission and other authorities, Daido Steel separated its spring division and established Daido Spring in December of the same year on the premise that it would merge with NHK Spring. Thus, in May 1958, the merger between the NHK Spring and Daido Spring was realized.
As a result, Daido Spring's Kawasaki Plant became NHK Spring's Kawasaki Plant. At this time, capital was increased to 500 million yen, and the Company cemented its position as a leading spring manufacturer.
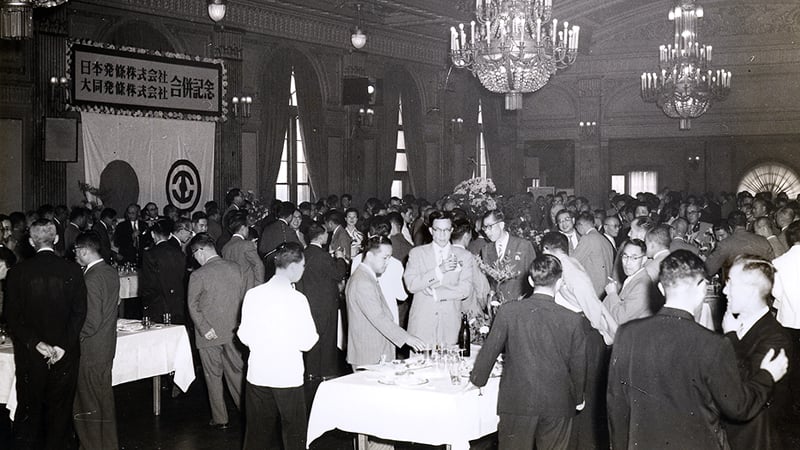

Merger with Daido Spring
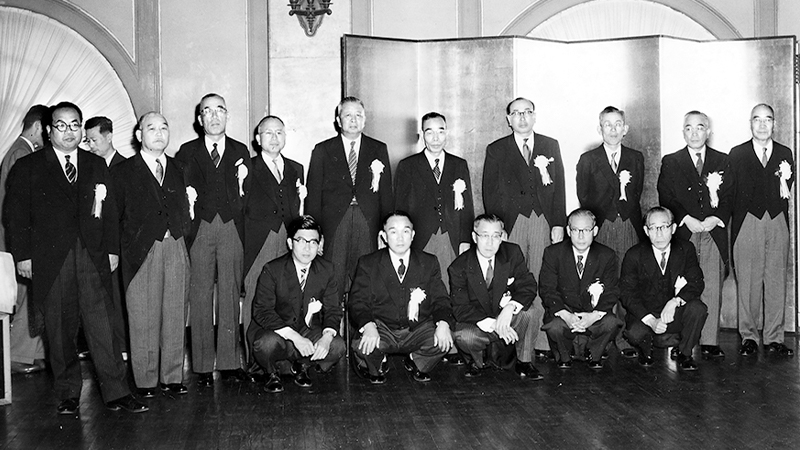

Top management at the time of merger
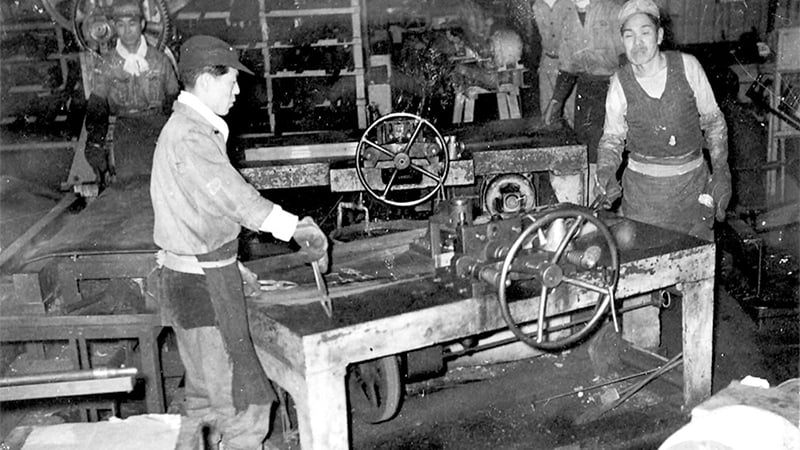

Production at Kawasaki Plant (Suspension Springs) immediately following merger
4. Entry into the seating business. From seat springs to production of urethane foam integrated seats
From 1949, the Company manufactured seat springs for jeeps for the Occupation Forces at the Miyada Plant (now Ina Plant) in Nagano Prefecture.
The company then expanded its business to include general trucks, etc., but as production volume increased, transportation costs began to mount, affecting profitability. The only way to overcome this situation was to build a new plant specializing in seat springs in a location adjacent to an automobile manufacturer.
This resulted in the establishment of the Nagoya Plant (current Toyota Plant) as the Company's first local production base in 1961.
The following year, the Kawasaki Plant (Seating) was established. At that time, the Company produced drum-shaped springs, however, through a technical tie-up with the American company Rockwell Corporation, it switched to S-springs, which improved productivity and reduced weight, giving us a head start over other spring manufacturers in making this type of spring. After that, in 1964, we started production of urethane foam integrated seats. After that, the seating business steadily expanded, including the establishment of the Ota Plant (current Gunma Plant).
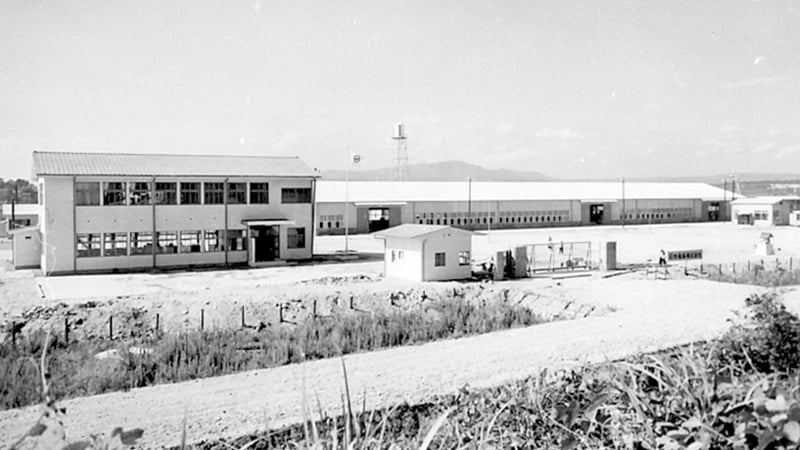

Full-scale entry into the automotive seating business (Nagoya Plant)
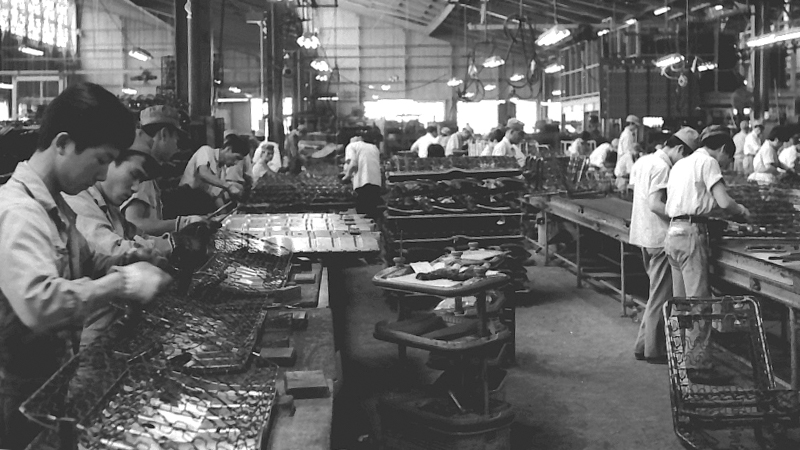

Newly established mass production Nagoya Plant
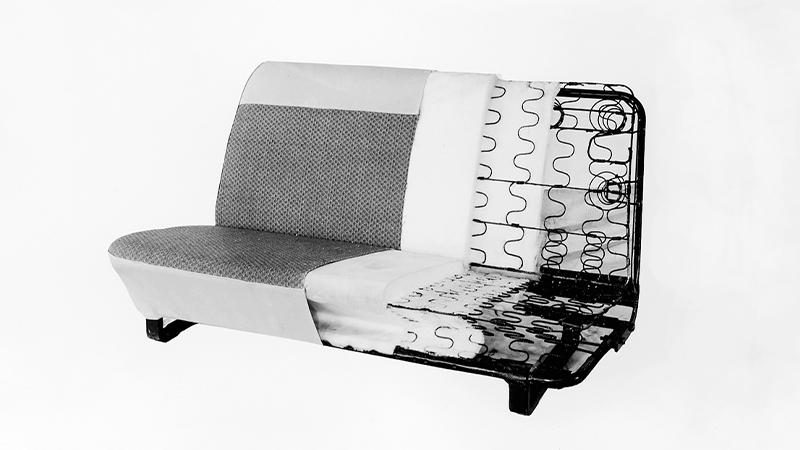
Produced urethane foam integrated seats
5. Overseas advances with no hesitation, starting with establishment of NHK Spring (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
In 1963, NHK Spring became the first automotive parts manufacturer to establish operations in Thailand (Note).
As early as the late 1950s, inquiries for leaf springs were coming in from Southeast Asia and South America, and the Company was beginning to establish a foothold in overseas production. At that time, the demand for springs in Southeast Asia was mainly for repair work. Whereas the domestic demand for springs was 300 tons, the Company was exporting 100-150 tons. Against this backdrop, the relevant directors at that time conducted exhaustive negotiations and eventually obtained approval to establish NHK Spring (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
Initially, the Company planned a facility with monthly production capacity of 400 tons of leaf springs. When it was first established, the plant had 101 employees comprising 94 locals and 7 expatriates from Japan.
NHK Spring (Thailand) Co., Ltd. has since established bases in various regions and started integrated production of seating, coil springs, and various precision springs, and has expanded its business beyond the automotive field to handle NHK Spring's main business such as HDD suspensions. The company is making great strides as one of the most important members of our group.
(Note) Yazaki Corporation entered Thailand earlier than NHK Spring, however, NHK Spring was the first to establish operations in Thailand in the automotive parts business.
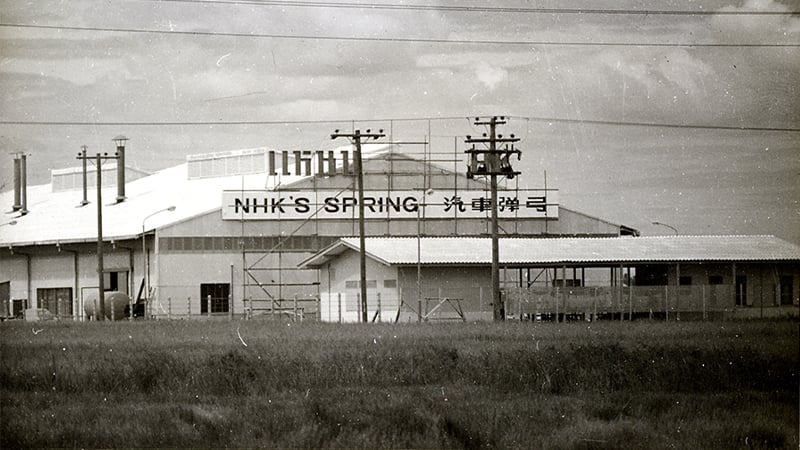

First overseas advance. Establishment of NHK Spring (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
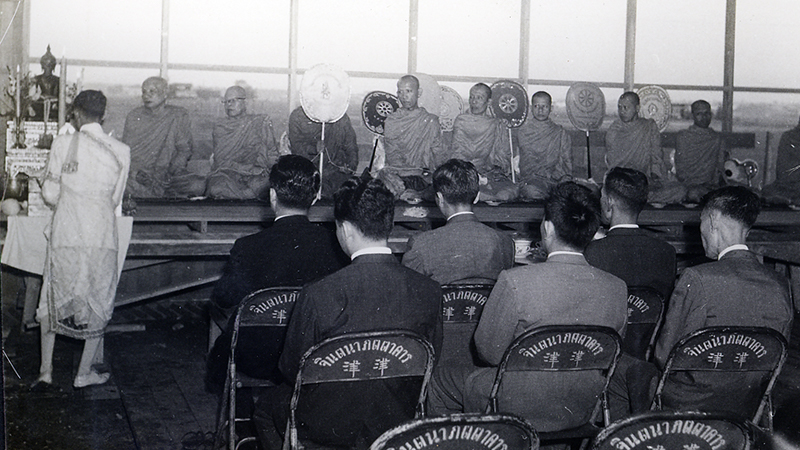

August 30, 1963: NHK Spring (Thailand) Co., Ltd. groundbreaking ceremony conducted in the Buddhist style
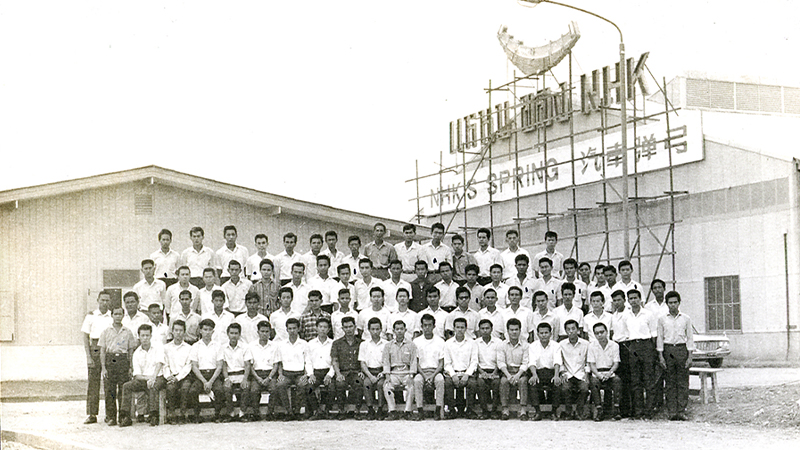

November 12, 1963: First initiation ceremony at NHK Spring (Thailand)
6. Diversification of the business. Expansion beyond manufacturing for corporate development
A surprisingly little-known fact is that NHK Spring used to operate a bowling alley and a cab company. Hisashi Sakamoto, the third President and CEO, and Kiyotoshi Fujioka, the fourth President and CEO, who were involved in the Company's founding, promoted diversification of the business, believing that "the future would be difficult if we were only a spring manufacturer. "Kinko Bowl" and "Kinko Kotsu" were representative Group companies at that time.
"Kinko Bowl" was operated in Isogo Ward, Yokohama during the bowling boom of the time, but it was later closed and turned into the Negishi Branch, where the Industrial Machinery and Equipment Division (at the time) had its offices. It has since been sold and no trace of the company remains. In addition, the cab company "Kinko Kotsu" was spun off from the NHK Spring Group and continues to operate today.
The ideas of our founders were rooted and passed down to other companies as well, such as Nippon Shaft, which develops and produces golf shafts and metal bats, and NHK MEC, which handles ship products. The breadth of the Group's current operations may be traced back to these days.
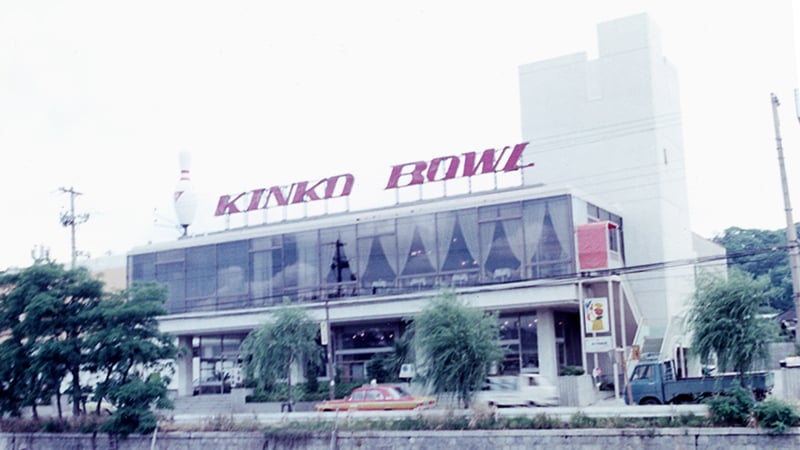

Kinko Bowl formerly operated by NHK Spring
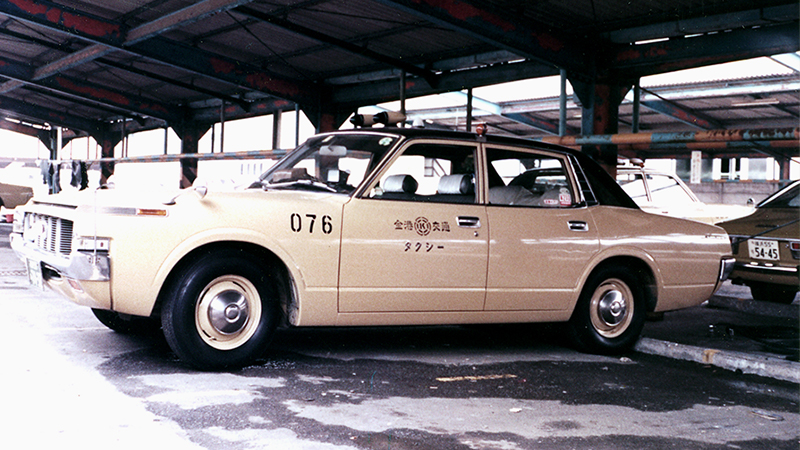

A taxi of Kinko Kotsu formerly operated by NHK Spring

Golf shafts produced by Nippon Shaft
7. Strengthen the precision spring business. Compete with more precise and advanced products and production technologies
Our small springs have developed mainly at our Miyada Plant (now Ina Plant) in Nagano Prefecture. Demand for both wire springs and sheet springs has been increasing since the 1960s. In order to make a full-scale entry into the field of precision springs, in which we had lagged behind, we established a two-plant system at Ina (renamed Ina Plant in 1963) and Kawasaki.
However, unlike suspension springs and seating, because small springs did not require large facilities and could be established with a small amount of capital, numerous small businesses shot up. In these circumstances, since the Company could not compete in terms of price, it had no choice but to compete based on product precision and more advanced production technology. It installed a large number of state-of-the-art high-precision machine tools and molding machines at both the Ina and Kawasaki plants.
Later, during the first and second phases of rationalization, the Company established production technology, including the introduction of automatic machines. In 1970, the precision springs business of the Kawasaki Plant was transferred to the Atsugi Plant in Kanagawa Prefecture. Thus, the precision springs business continued to expand, with Atsugi Plant producing thin leaf springs and Ina Plant producing wire springs as the main products.
In 2000, the HDD suspensions business, which had been a part of the precision spring business, was spun off as the DDS Business Division.
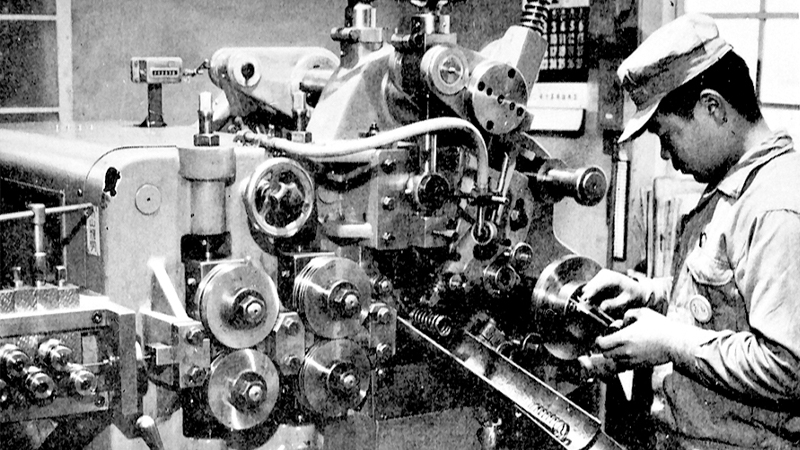
Introduction of state-of-the-art coiling machines
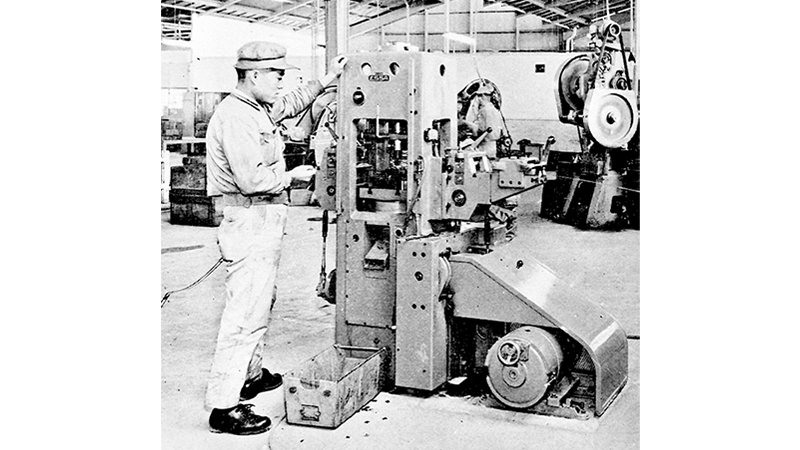
Automatic precise stamping machine for thin sheet springs introduced as a part of rationalization
In 1970, the precision springs business was transferred from Kawasaki to the Atsugi Plant.
8. Development of non-automotive fields. Developing a wide variety of new products in various fields
In 1971, our first medium-term management plan, “Vision 5,” was announced and set high numerical targets. The next plan, “New Vision 5” announced in 1976, set even higher numerical targets. To achieve these targets, the plan clearly stated that the Company would not only rely on the automotive field, which had previously accounted for a high percentage of its sales, but would also “increase sales of products other than existing automotive-related products to 40% of total sales. We have entered an era of full-fledged business diversification.
The pioneer of the Industrial Machinery and Equipment business was pipe hangers for plant piping support equipment. Subsequently, pipe clamps, mechanical snappers, and disc springs used in the Honshu-Shikoku bridges were developed and produced. The Komaki Plant in Aichi Prefecture, which was newly established in 1980, produced mechanical multilevel parking equipment (production was later moved to the Yasu Plant in Shiga Prefecture). The chemical products business became the next pillar of focus after the plant division. Various developments were carried out and consolidated in Komagane, Nagano Prefecture. In 1986, the Electronic Components Department was newly established and began production of integrated metal substrates. In 1990, we launched a brazing business, which has grown into today's bonding and ceramics business. The security business grew out of the information-related equipment business and has earned the Company a worldwide reputation for its anti-counterfeiting technology.

Pipe hangers (Atsugi Plant at that time), which grew into the Industrial Machinery and Equipment business
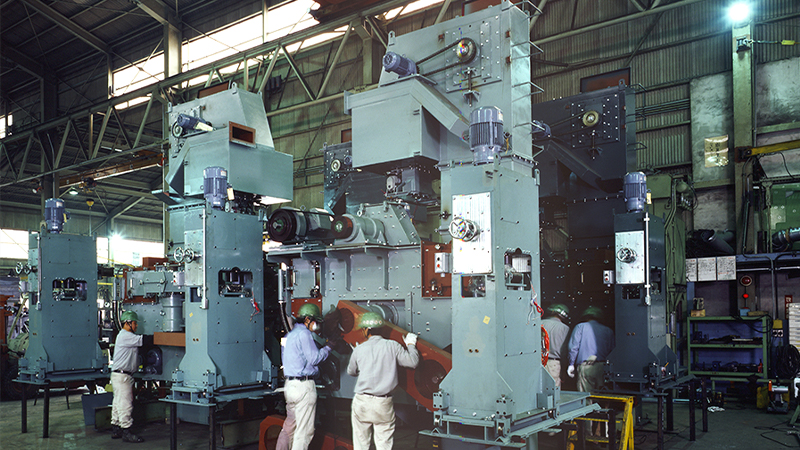
Komaki Plant, which was newly established to produce large-size devices in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment business

Chemicals business, consolidated into Komagane Plant
9. Major relocation to new premises in Yokohama. Consolidation of the Isogo and Kawasaki production bases into Kanazawa Ward
Planning for the Trans-Tokyo Bay Expressway began in the 1960s, and since it runs through the land of our former Head Office/Yokohama Plant (Isogo Ward at the time), we decided to cooperate with the City of Yokohama by accepting an alternative site. Although the oil crisis and other factors delayed the initial plan, in 1979, it was decided to secure a landfilled site in Kanazawa Ward, Yokohama. In response, a preparatory office for the construction of the new Yokohama Plant was established the following year, and the relocation plan was launched in earnest.
In 1987, construction of a plant for automobile suspension coil springs began, followed by the construction of a seating block the following year. In parallel with the above, the NN Planning and Promotion Office was established to plan the use of the entire new site, and the Main Building, the Development and Experiment Building, the Welfare Building, and the Employee Pension Fund Hall (now the gymnasium) were constructed.
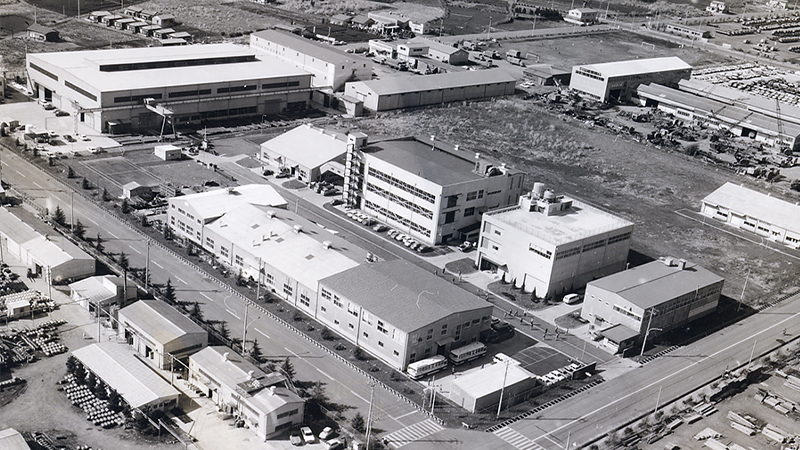
In 1991, the Head Office, Yokohama Plant, Kawasaki Plant, Negishi Branch, and NHK Spring Group Central Research Laboratory all moved to the new Yokohama Works, where they remain to this day.
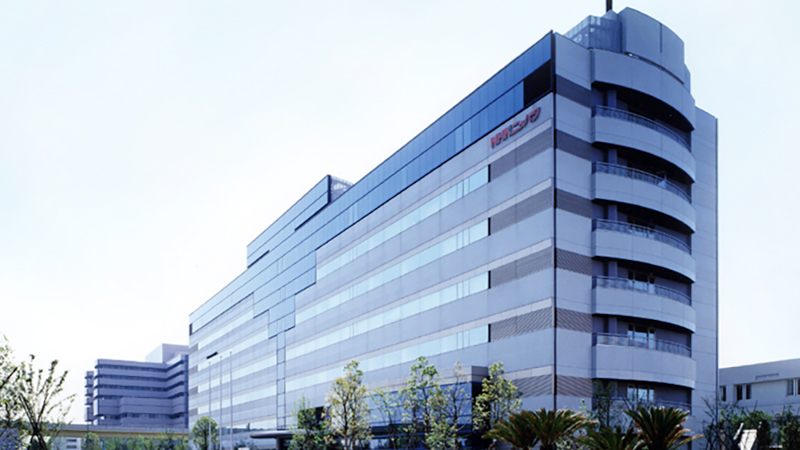

Head Office relocated in 1991
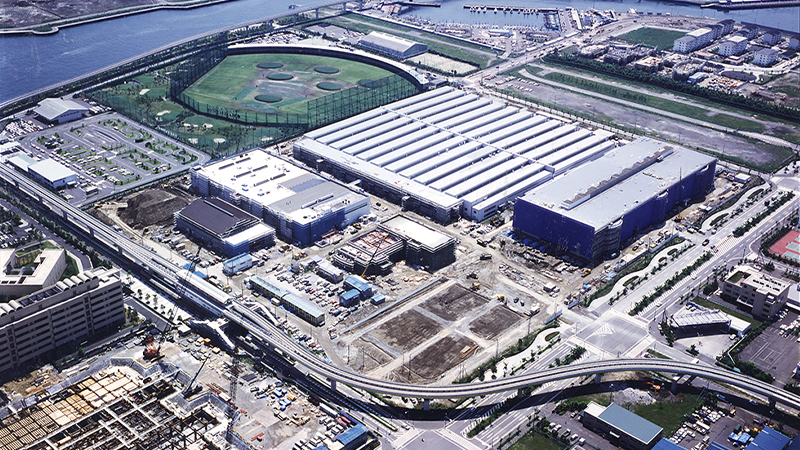

Yokohama Office under construction in 1989. The main building has not yet been constructed.

Development laboratory immediately after completion
10. Aggressive global deployment of the Group. Establishment of bases in a series of new locations
In the 2000s, the Company experienced various hardships such as the economic downturn precipitated by the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy, the Great East Japan Earthquake, and massive flooding in Thailand, but our Group as a whole continued to grow steadily. In Japan, we reorganized our Group companies and expanded our business by developing highly competitive products in a wide range of fields. Overseas, we established bases for suspension springs, automotive seating, and precision springs in China and other countries.
In the 2010s, we accelerated our global activities by establishing new bases in the Philippines, Indonesia, Mexico, and other countries and regions we had not previously entered. In 2015, we also established our first production base in Eastern Europe, in Hungary, as a foothold for expanding sales to European manufacturers. Our global expansion is based on "local production for local consumption" rather than, for example, entering a market because labor costs are low, and our unchanging desire is to be loved as a local company rooted in each community.

NHK Spring Hungary KFT., our first production base in Europe

NHK Spring Mexico S.A. DE C.V. in joint development with Group company Topura Co., Ltd.
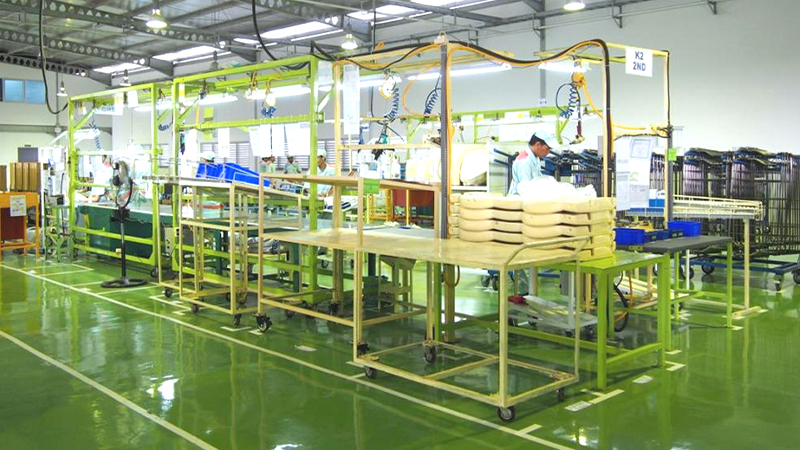

Seat production in Indonesia