NHK Spring Group's Global Environmental Conservation Activities
NHK Spring Group's Environmental Challenges
In an effort to contribute to global environmental conservation, NHK Spring has earmarked construction of a decarbonized society based on reduction of CO₂ emissions, and realization of zero industrial waste, as materialities (important issues).
Since publishing the Environmental Voluntary Plan in 1993, the entire NHK Spring Group has been involved in global environmental conservation activities. To further clarify NHK Spring Group's future role in helping to realize a sustainable society, the President & CEO personally declared "NHK Spring Group's Environmental Challenges" in September 2021.
Currently, a roadmap has been formulated in accordance with the medium-term goals for up to FY2026, and the Company checks the progress of activities and promotes initiatives while discussing reduction measures through the Global Environmental Response Committee. In addition, review is being advanced concerning the clarification of governances related to climate change, analysis of risks and opportunities, establishment of risk management and so on.
NHK Spring Group's Environmental Challenges
① Achieve carbon neutrality by 2039.
To this end, reduce CO₂ emissions by 50% from the FY2013 level by 2030.
② Aim to realize zero industrial waste by 2039.
To this end, reduce industrial waste by 95% compared to FY2013 by 2030.
CO₂ and Industrial Waste Emissions and Main Measures geared to Reduction
|
Item
|
Results (FY2021) |
Results (FY2022) |
Main Measures Geared to Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CO2
(thousand tons-CO₂)
|
157 |
136 |
Promotion of energy saving, and technical innovation in electrification of equipment/production processes and product development |
|
Industrial waste
(thousand tons)
|
45.6 |
48.6 |
Re-examining of recycling contractors/Promotion of free recycling and conversion of waste materials into valuable resources |
Targets for totaling: NHK Spring and consolidated subsidiaries in Japan
Governance
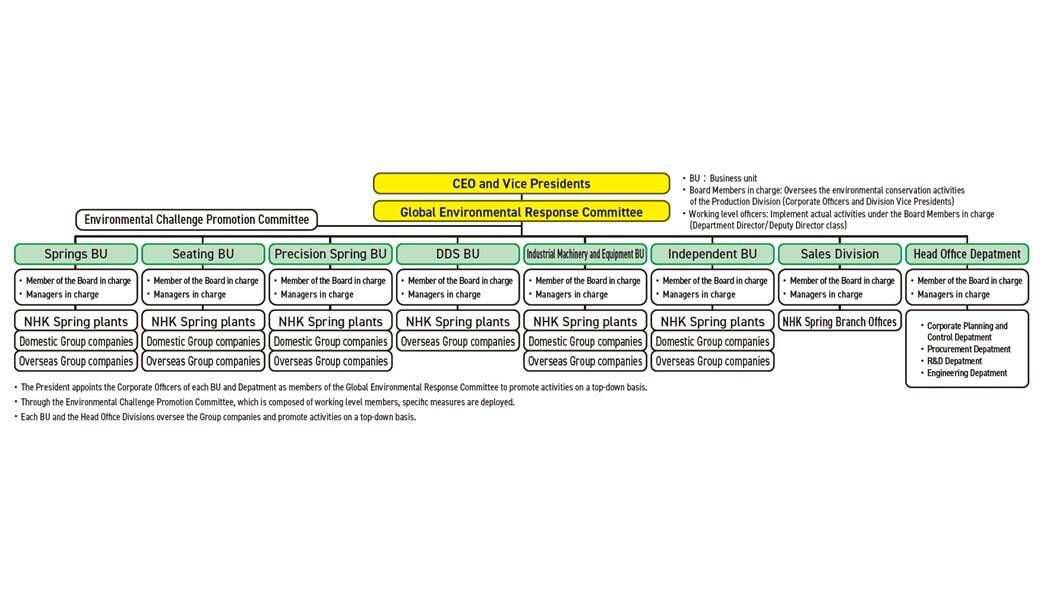
Based on the declaration, the Global Environmental Response Committee has compiled a long-term plan of environmental activities for each business and strengthened activities with a view to realizing a sustainable society in NHK Spring Group.
The Global Environmental Response Committee meets two times a year. The Committee sets medium- to long-term goals related to the Environmental Challenges, and compiles scenarios and promotes activities for realizing them. It periodically reports on the progress of activities to the Management Committee so that they can be reflected in the management strategy.
Strategy
In NHK Spring Group, each Production Division and the Group companies have established numerical goals for FY2026, and they implement specific measures categorized as "Energy saving", "Electrification of equipment", "Technical innovation in production processes and product development", "Plant investment in solar power generation, etc.", and "Purchase of electric power derived from renewable energy" following exhaustive review in the Investment and Loan Committee. The Global Environmental Response Committee receives ongoing reports from each Production Division and the Group companies and monitors the degree of progress in relation to the planned activities.
Moreover, through the Electrification Business Promotion Department that was inaugurated in April 2018, we supply products that contribute to the reduction of CO₂ emissions.
<Physical risks> Risks related to physical impacts such as disasters, etc. caused by climate change
|
|
Influencing Factors |
Risks |
Opportunities |
Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Acute
|
・Major disasters caused by abnormal weather |
・Production disruption caused by river flooding, massive typhoon, drought, tsunami, high tide, lightning strike, etc. |
・Gaining of customers' trust and expansion of orders through strengthening of BCP measures |
・Tsunami evacuation facilities and displaying of height above sea level in various locations |
|
Chronic
|
・Meteorological information |
・Quality problems arising from insufficient product durability occurring in line with warming |
・Improvement of added value and profits based on enhancement of product durability |
・Tsunami evacuation facilities and display of elevation above sea level in various locations |
|
Policies/Regulations |
・Electrification promotion measures (ZEV*1, fuel, gasoline vehicle regulations) |
・Acceleration in development of eco cars by customers, leading to reduced sales of parts for gasoline vehicles |
・Increased sales thanks to progress in development of products for EV/FCEV*4 (ZEV) |
Development of EV/FCEV products and parts |
|
Market |
・Expansion of CASE and MaaS market |
・Decline in sales of conventional products due to changes in the value and methods of use of automobiles |
・Creation of added value and establishment of superiority and business opportunities through products and services supplied to the market as a result of advanced initiatives to address climate change and development of energy saving products |
・Promotion of cutting-edge research and development with a view to the future of semiconductors and electronics |
|
Technology |
・Energy conversion |
・Increased costs and financial burden in production technology fields in line with energy conversion |
・Expansion of business and improvement of profits due to development of energy saving and lower cost production in the manufacturing phase |
・Promotion of energy optimization in plants |
|
Reputation |
・Changes in customers' evaluations |
・Failure to win orders due to inability to cater to demands for products with small environmental load (decarbonization, etc.) |
・Greater superiority compared to competitors, and increased orders thanks to development of decarbonized products |
・Development of environmentally considerate materials and design of products |
* 1 ZEV: Acronym for Zero Emission Vehicle. This refers to EVs/FCEVs, etc. that emit no carbon gases, etc. when running.
* 2 CP: Acronym for Carbon Pricing. This refers to the pricing of carbon based on carbon tax and emissions trading.
* 3 GX: Acronym for Green Transformation. This refers to transformation that is geared to reduction of emissions and improvement of competitiveness based on viewing initiatives for achieving greenhouse gas emission reduction goals as opportunities for growth.
* 4 FCEV: Acronym for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle.
* 5 GHG: Acronym for Greenhouse Gas. This refers to CO₂ and other greenhouse gases.
Risk Management
NHK Spring has built a risk management structure having the President & CEO and Representative Member of the Board as the chief responsible officer and the President of the Corporate Planning and Control Division in charge of promotion. Through this structure, we manage risks including those related to climate (physical risks and transition risks).
In conducting risk management, we decide measures and manage progress with a view to averting risks, minimizing damage, and preventing recurrence.
Meanwhile, recognizing the need to build a governance process clearly involving the Board of Directors in risk management, we will take concrete steps in this area too.
Indicators and Goals
NHK Spring Group has set reduction targets for CO₂ emissions calculated according to the amount of energy consumption, and we are committed to implementing global environmental conservation activities. Up to FY2020, we managed our CO₂ emissions per unit of sales, but since FY2021 we have switched to managing based on total emissions in order to achieve carbon neutrality.
Medium- and Long-term Goals
| Item | Target year | Target value |
| CO₂ Emissions | 2030 | CO₂ emissions in SCOPE 1*6 + SCOPE 2*7 50% down compared to FY2013 |
| 2039 | Zero CO₂ emissions in SCOPE 1 + SCOPE 2 | |
| Amount of Industrial Waste | 2030 | 95% reduction compared to FY2013 |
| 2039 | Aiming for zero industrial waste |
* 6 SCOPE 1: CO₂ emissions from use of fuel by business operators
* 7 SCOPE 2: CO₂ emissions from use of electric power, etc. supplied by other companies